Energy Hub project
Energy Hub is the multi-port energy system for electric vehicle charging
General Description
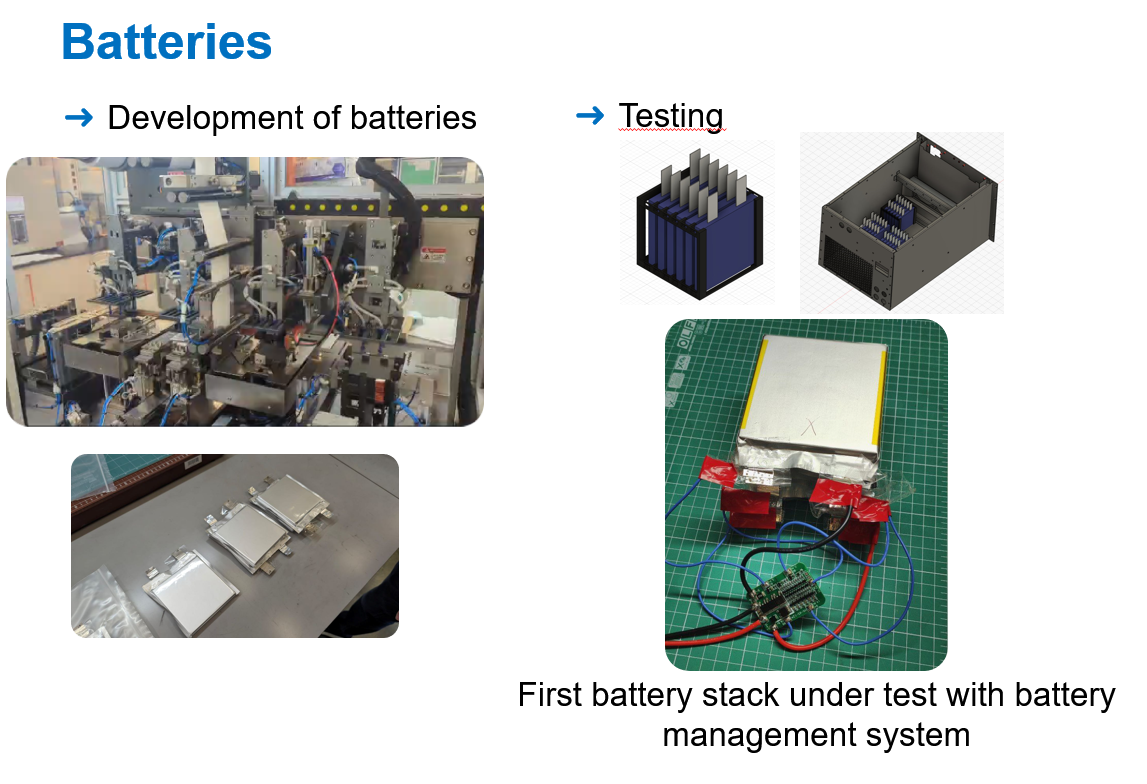
Energy Hub is an advanced fast electric vehicle charger with uses an inner battery to minimize the impact of the charging process in the grid. In addition, the charger uses a novel multi-port converter with a unique control algorithm which allows to control the power flow between the grid, the inner battery and the electric vehicle with all of them galvanically isolated. The project includes the developments of fully controllable 4-quadrant inverters, multi-port DC/DC converters and batteries.
The technical result consists in increasing the efficiency of the charger, ensuring a bidirectional flow of electricity and bidirectional connection of several DC sources to one device, reducing network overload, increasing safety, and also in simplifying it and increasing reliability.
 |
 |
 |
IP Protection
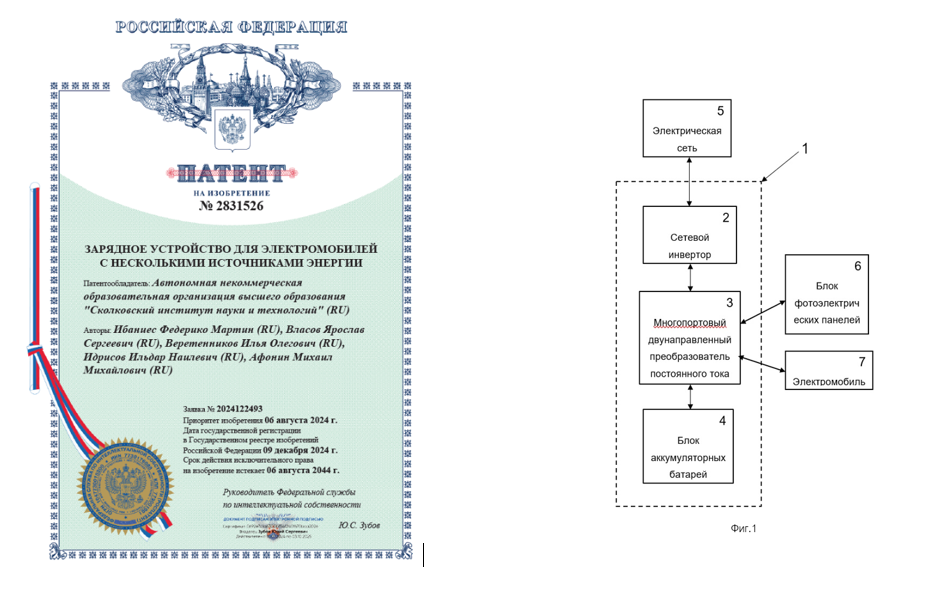
The Energy hub invention was patented in 2024 year.
Industrial Impact
This electric vehicle charger is a unique demonstrator of the power electronic capabilities for dealing with multi sources and several loads. The multiple active bridge converter with the proposed control allows following:
– user can charge an internal battery with solar panels;
– to sell energy to the grid;
– to charge the vehicle fast with the stored energy in the internal battery and the renewable energy available minimizing the power from the grid;
– vehicle to grid (V2G) operation for future power transfer;
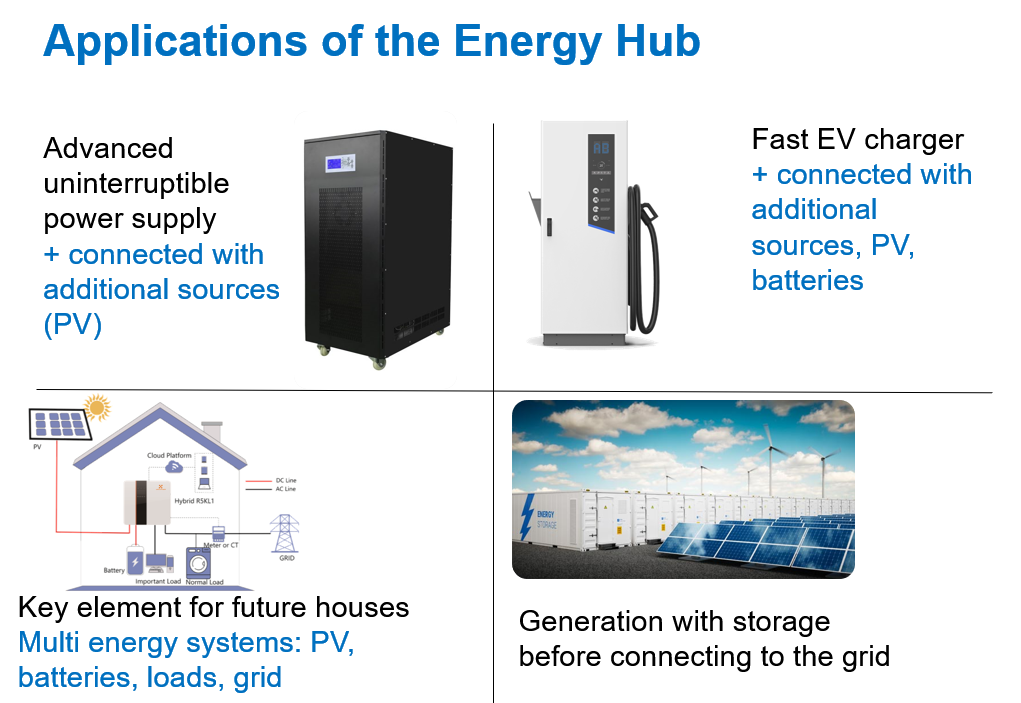
This is the unique product and can be exploited in many other areas such as:
– uninterruptible power systems in which at least three ports are needed: battery, grid and load but more devices can be added such as a PV panel;
– inside the electric vehicle, were there are several loads at different voltages to control such as the power motors, controllers, auxiliary systems, air conditioning, etc. Each of them can be a port in the multiport system;
– domestic energy storage systems, in which there are PV panels, batteries and different loads;
– avionics, in which you might have different voltage levels and redundant sources.
Scientific Novelty
The Energy Hub project introduces a new circuit topology for using more than two ports in power electronics. Usually, power converters which transforms alternating to direct current or direct current to direct current at different voltages has only two ports: input and output. Some of the most advanced converters have a bidirectional powerflow in which input and output ports can be exchanged, so energy can flow in both directions. Multiport systems have three or more ports, in which you can connect different assets as loads or sources.
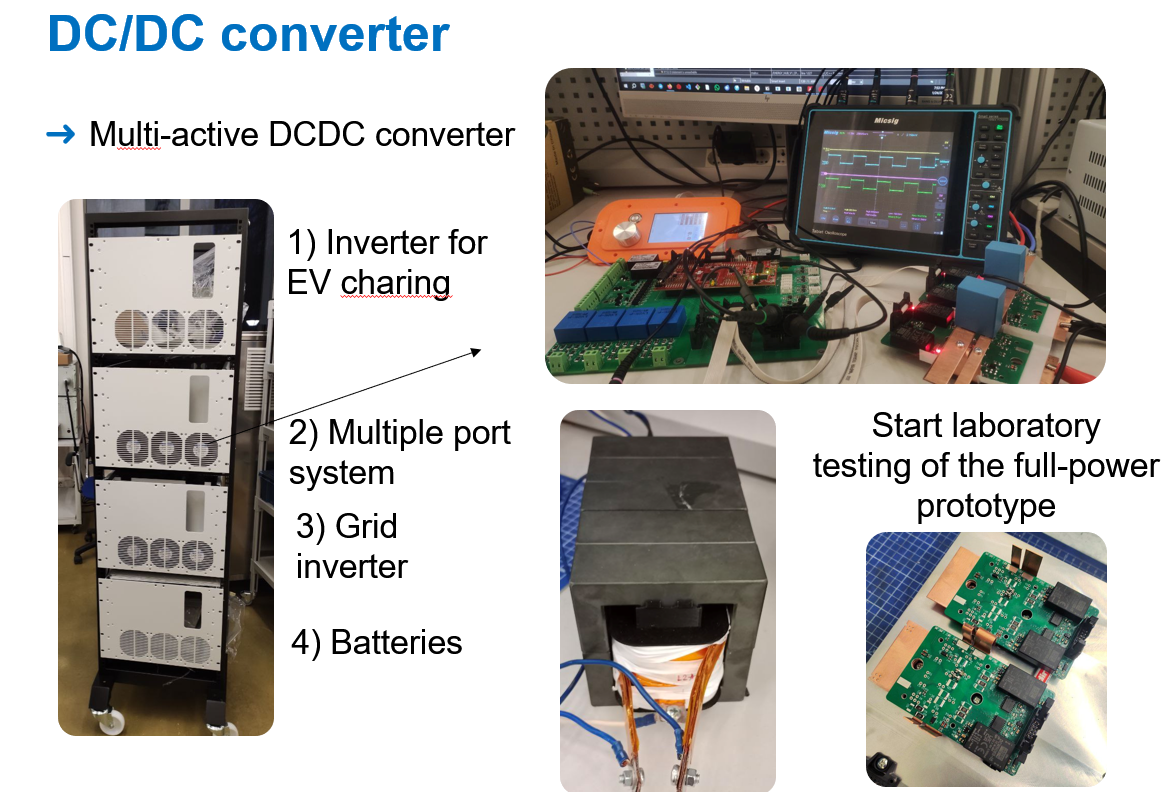
The novelty in the Energy Hub is the introduction of a single converter with multiple ports and galvanic isolation: the multiple active bridge converter. The power electronics team have developed an special control technique with allowed the converter to work with any number of ports without increasing the control complexity.
The multiple active bridge converter gives galvanic isolation to each port, which is very important for safety issues and it is mandatory in electric vehicle chargers. In addition, bidirectional power flow is allowed in each port so the vehicle can be used as a source to charge another vehicle, the grid, or an internal battery.
The energy hub consists in the multiple active bridge converter which four ports: one for a renewable source as solar panels, one for an internal battery, one for the electric grid and one for the vehicle. However, these ports can be adapted for other applications. Using this novel converter, the energy demanded for the vehicle can be delivered partially from the grid, partially from the internal battery and partially from an external source as a solar panel.
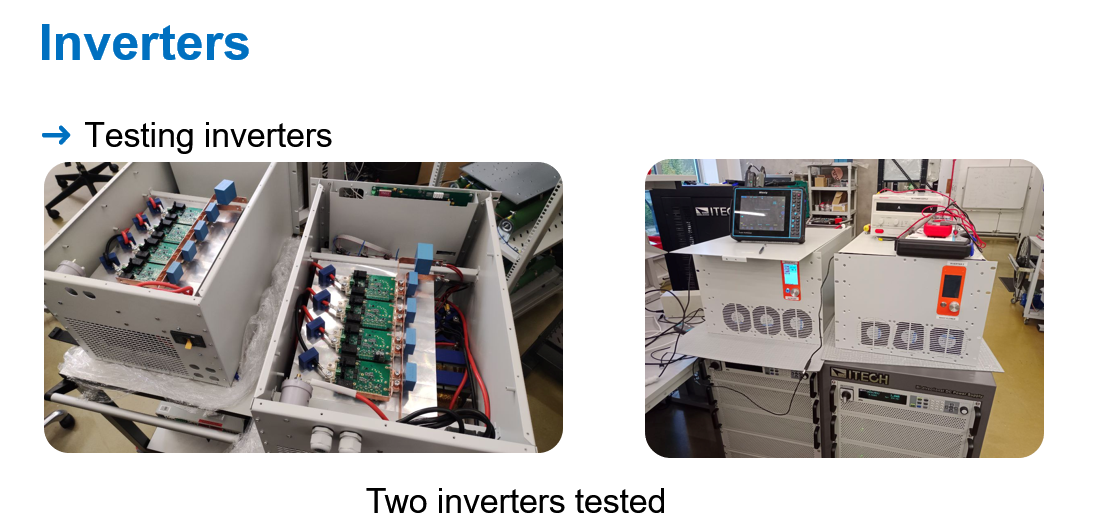
Finally, it is worth to mention that Energy Hub requires an inverter to transform the AC power from the electric grid to a direct current power flow which can be managed by the multiple active bridge converter. The converter only works with DC power. For that, two 4-quadrant inverters were developed. Those inverters have an advanced control which allows them to work as a source or as a load. As a source the can use the energy from the vehicle to provide electricity and as a load it works as a standard charger. The source mode is quite novel because it allows to work with another inverters sharing the power.
The control of both converters have been published in the frame of the Energy Hub project and a patent will be submitted in the third term of 2024.
Research outcomes
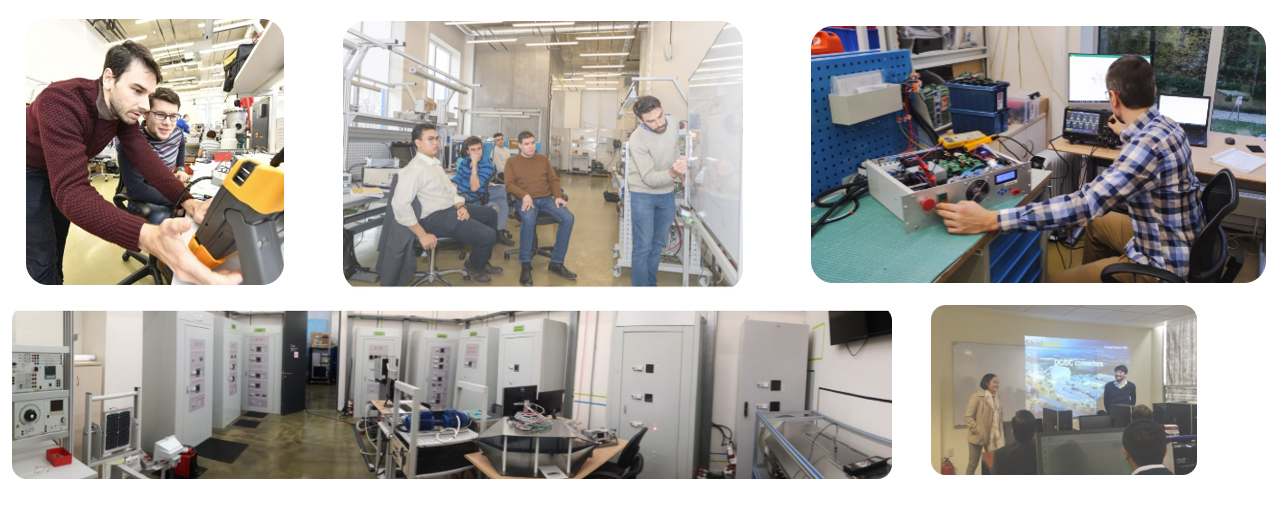
Laboratory
Energy Hub is developing in the Smart grid Laboratory of the Center for Energy Science and Technology (SKOLTECH).